We are going to see how to exploit Jsonb field types from PostgreSQL in a generated interface of Sonata.
We start with the assumption that you already master the basic concepts of Symfony, Sonata, and PostgreSQL.
First, let's create a simple table in PostgreSQL that will contain a Jsonb field.
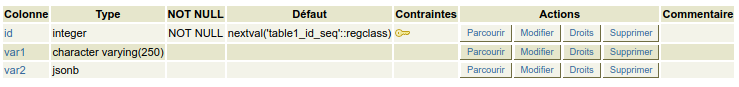
CREATE SEQUENCE public.table1_id_seq;
CREATE TABLE public.table1 (
id integer DEFAULT nextval('public.table1_id_seq'::regclass) NOT NULL,
var1 character varying(250),
var2 jsonb
);
ALTER TABLE ONLY public.table1
ADD CONSTRAINT table1_pkey PRIMARY KEY (id);
Then, generate the entity and its admin interface
php bin/console doctrine:mapping:import "App\Entity" annotation --path=src/Entity
php bin/console make:entity --regenerate App
php bin/console make:sonata:admin App/Entity/Table1
We notice the field type in our entity
<?php
namespace App\Entity;
use Doctrine\ORM\Mapping as ORM;
/**
* Table1
*
* @ORM\Table(name="table1")
* @ORM\Entity
*/
class Table1
{
/**
* @var int
*
* @ORM\Column(name="id", type="integer", nullable=false)
* @ORM\Id
* @ORM\GeneratedValue(strategy="SEQUENCE")
* @ORM\SequenceGenerator(sequenceName="table1_id_seq", allocationSize=1, initialValue=1)
*/
private $id;
/**
* @var string|null
*
* @ORM\Column(name="var1", type="string", length=250, nullable=true)
*/
private $var1;
/**
* @var json|null
*
* @ORM\Column(name="var2", type="json", nullable=true)
*/
private $var2;
public function getId(): ?int
{
return $this->id;
}
public function getVar1(): ?string
{
return $this->var1;
}
public function setVar1(?string $var1): self
{
$this->var1 = $var1;
return $this;
}
public function getVar2(): ?array
{
return $this->var2;
}
public function setVar2(?array $var2): self
{
$this->var2 = $var2;
return $this;
}
}
And our generated admin interface in its simplest format
<?php
declare(strict_types=1);
namespace App\Admin;
use Sonata\AdminBundle\Admin\AbstractAdmin;
use Sonata\AdminBundle\Datagrid\DatagridMapper;
use Sonata\AdminBundle\Datagrid\ListMapper;
use Sonata\AdminBundle\Form\FormMapper;
use Sonata\AdminBundle\Show\ShowMapper;
final class Table1Admin extends AbstractAdmin
{
protected function configureDatagridFilters(DatagridMapper $datagridMapper): void
{
$datagridMapper
->add('id')
->add('var1')
->add('var2')
;
}
protected function configureListFields(ListMapper $listMapper): void
{
$listMapper
->add('id')
->add('var1')
->add('var2')
->add('_action', null, [
'actions' => [
'show' => [],
'edit' => [],
'delete' => [],
],
]);
}
protected function configureFormFields(FormMapper $formMapper): void
{
$formMapper
->add('id')
->add('var1')
->add('var2')
;
}
protected function configureShowFields(ShowMapper $showMapper): void
{
$showMapper
->add('id')
->add('var1')
->add('var2')
;
}
}
Our goal now is to create a nested form structure to manage our data in json.
For this, we will use Symfony's collections.
The steps are the following: we will create a form that will be integrated into the field. It will have an add/remove button to add items to our collection.
We will then link our form to our field "var2".
We create our form in the Form directory of src.
<?php #src/Form/fieldvar2.php
namespace App\Form;
use Symfony\Component\Form\AbstractType;
use Symfony\Component\Form\FormBuilderInterface;
use Symfony\Component\OptionsResolver\OptionsResolver;
use Symfony\Component\Form\Extension\Core\Type as FormType;
class fieldvar2 extends AbstractType
{
public function buildForm(FormBuilderInterface $builder, array $options)
{
$builder
->add('var2_titre', FormType\TextType::class, [
'label' => 'Var2 titre',
])
->add('var2_valeur', FormType\TextType::class, [
'label' => 'var2 valeur',
]);
}
public function configureOptions(OptionsResolver $resolver)
{
}
}
?>
Then, we need to link this form to our field.
use Symfony\Component\Form\Extension\Core\Type as FormType;
use App\Form\fieldvar2;
final class Table1Admin extends AbstractAdmin
{
protected function configureFormFields(FormMapper $formMapper): void
{
$formMapper
//->add('id') #on supprime le champs id puisqu'il est auto incrémenté
->add('var1')
->add('var2', FormType\CollectionType::class, [
'allow_add' => true,
'allow_delete' => true,
'entry_type' => 'App\\Form\\fieldvar2',
'label' => 'Var jsonb',
])
;
}
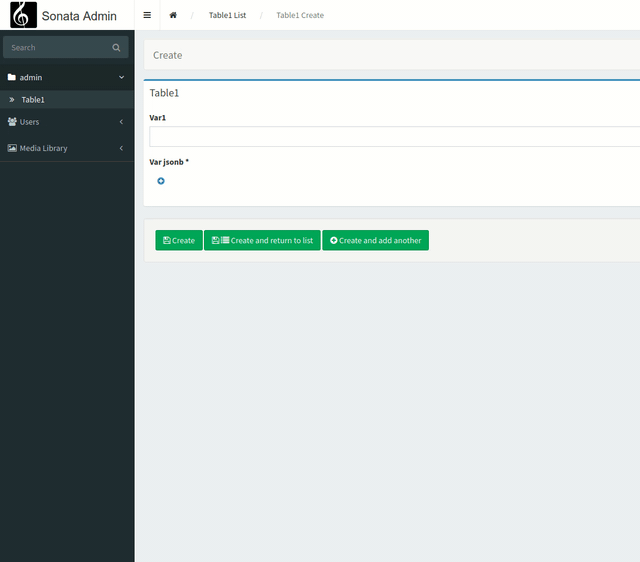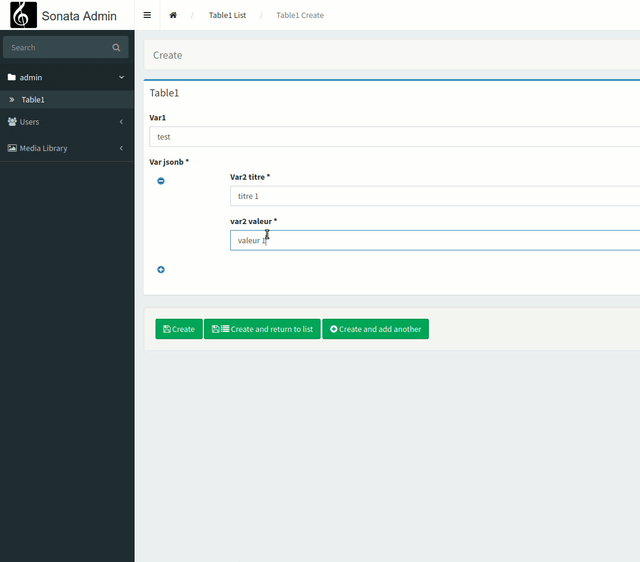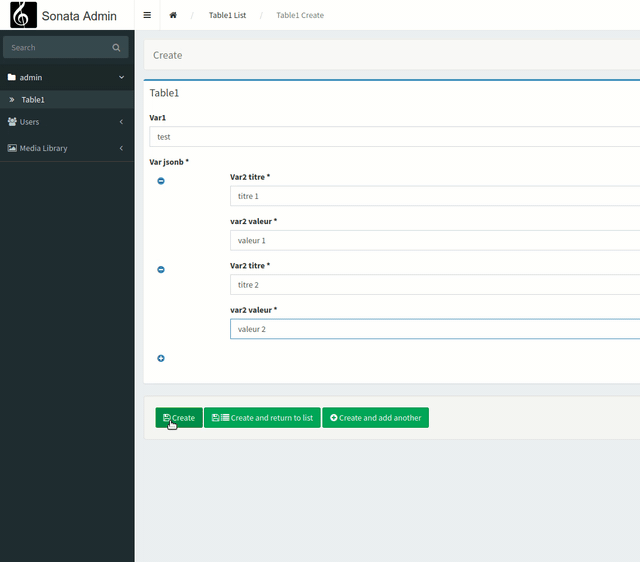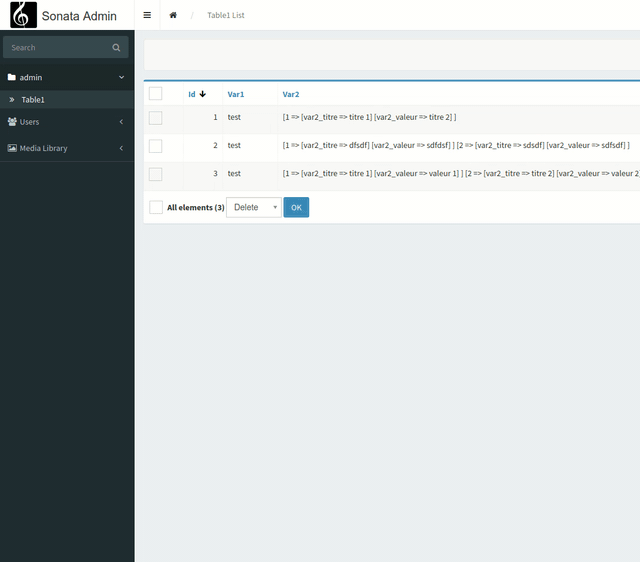
Now we are going to see how we could have a nesting of forms within our form. In other words, "nested collections".
And for this, we will have to use a Sonata Collection component because it is the only one that will work with multiple nestings (theoretically, infinitely).
We will add the reference to Sonata\AdminBundle\Form\Type\CollectionType, create a second form, and implement it in our first form.
<?php #src/Form/fieldvar2valeur.php
namespace App\Form;
use Symfony\Component\Form\AbstractType;
use Symfony\Component\Form\FormBuilderInterface;
use Symfony\Component\OptionsResolver\OptionsResolver;
use Symfony\Component\Form\Extension\Core\Type as FormType;
class fieldvar2valeur extends AbstractType
{
public function buildForm(FormBuilderInterface $builder, array $options)
{
$builder
->add('valeurs_multiples', FormType\TextType::class, [
'label' => 'Netsted 2 val',
]);
}
public function configureOptions(OptionsResolver $resolver)
{
$resolver->setDefaults([
'allow_extra_fields' => true,
'allow_add' => true,
]);
}
}
?>
Our implementation of the level 2 collection
<?php #src/Form/fieldvar2.php
namespace App\Form;
use Symfony\Component\Form\AbstractType;
use Symfony\Component\Form\FormBuilderInterface;
use Symfony\Component\OptionsResolver\OptionsResolver;
use Symfony\Component\Form\Extension\Core\Type as FormType;
use App\Form\fieldvar2valeur;
use Sonata\AdminBundle\Form\Type\CollectionType;
class fieldvar2 extends AbstractType
{
public function buildForm(FormBuilderInterface $builder, array $options)
{
$builder->add('var2_titre', FormType\TextType::class, [
'label' => 'Var2 titre',
])
->add('var2_valeur', CollectionType::class, [
'allow_add' => true,
'allow_delete' => true,
'entry_type' => 'App\\Form\\fieldvar2valeur',
'label' => 'Data Nested 2',
])
;
}
public function configureOptions(OptionsResolver $resolver)
{
$resolver->setDefaults([
'allow_extra_fields' => true,
'allow_add' => true,
]);
}
}
?>
And all that's left is to modify the configuration of our collection to use the SonataAdmin component
<?php
declare(strict_types=1);
namespace App\Admin;
use Sonata\AdminBundle\Admin\AbstractAdmin;
use Sonata\AdminBundle\Datagrid\DatagridMapper;
use Sonata\AdminBundle\Datagrid\ListMapper;
use Sonata\AdminBundle\Form\FormMapper;
use Sonata\AdminBundle\Show\ShowMapper;
use App\Form\fieldvar2;
use Sonata\AdminBundle\Form\Type\CollectionType;
final class Table1Admin extends AbstractAdmin
{
protected function configureDatagridFilters(DatagridMapper $datagridMapper): void
{
$datagridMapper
->add('id')
->add('var1')
->add('var2')
;
}
protected function configureListFields(ListMapper $listMapper): void
{
$listMapper
->add('id')
->add('var1')
->add('var2')
->add('_action', null, [
'actions' => [
'show' => [],
'edit' => [],
'delete' => [],
],
]);
}
protected function configureFormFields(FormMapper $formMapper): void
{
$formMapper
//->add('id')
->add('var1')
->add('var2', CollectionType::class, [
'allow_add' => true,
'allow_delete' => true,
'entry_type' => 'App\\Form\\fieldvar2',
'label' => 'Var jsonb',
])
;
}
protected function configureShowFields(ShowMapper $showMapper): void
{
$showMapper
->add('id')
->add('var1')
->add('var2')
;
}
}
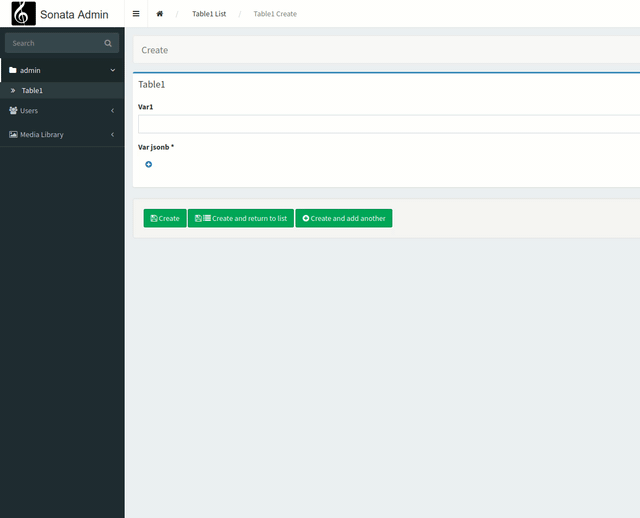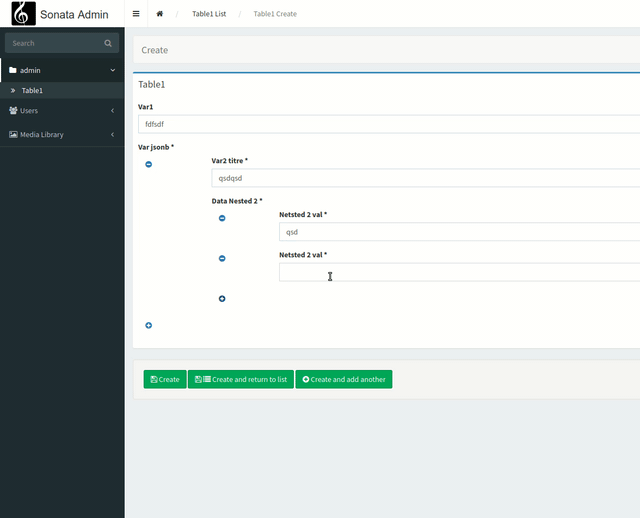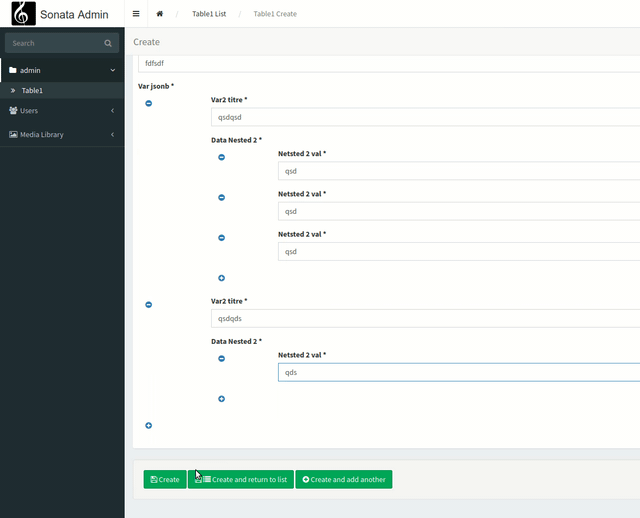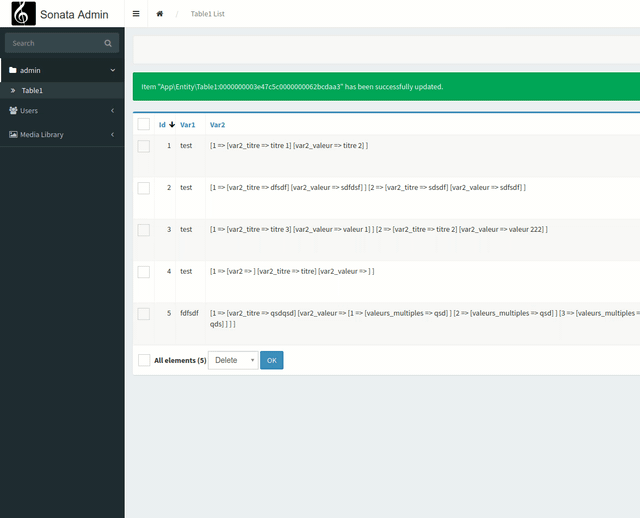
This is what it looks like